Application of a Real-Time Dashboard to Reduce Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in Intensive Care Units-Juniper publishers
JUNIPER PUBLISHERS-OPEN
ACCESS INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PULMONARY & RESPIRATORY SCIENCES
Abstract
Introduction and Purpose:
Ventilator-associated pneumonia is the second
most common nosocomial infection that develops in patients admitted to
the intensive care unit. The mortality rate for VAP ranges from 24% to
76% and is even higher than the primary illness. Based on the importance
of this issue, many organizations have focused on strategies and
guidelines to reduce the occurrence of complications such as ventilator
associated pneumonia. Despite these guidelines, due to multi orders with
different conditions and time periods, multi caregivers in the
intensive care unit and human mistakes, still there are high rates of
VAP. The purpose of this study is to provide an overview of real-time
dashboards applications which were designed and implemented as a
solution to reduce Ventilator-associated-pneumonia in Intensive Care
Unit.
The VAP reduction dashboards in different research
studies are implemented with real-time and visual data display features
which help caregivers to know the existing condition. So they can do the
necessary tasks. Besides, alerts and reminders are among the effective
features of this software.
Because of the representing order lists and the way
tasks are done, VAP reduction dashboards, will reduce human mistakes
regarding the time consumed and the way it is done. Also, representing
history of finished tasks prevents mistakes caused by coordination
between multiple caregivers, and finally clinicians begin to understand
the importance of consistency in the clinical documentation templates
and practices.
Finally, using mobile or web based version,
connecting dashboard to patient medical record, representing management
information, using sensor and hardware for data entry and connecting
dashboard to decision support system make VAP reduction dashboards more
effective.
Abbreviations: CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; CPOE: Computerized Provider Order Entry; EMR: Electronic Medical Record; HAIs: Hospital-Acquired Infections; ICU Intensive Care Unit; INICC: International Consortium Controlling Hospital Infections; LOS: Lengths of Stays; MDR: Multi-Drug-Resistant; VAP: Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia
Ventilator-associated pneumonia is the second most
common nosocomial infection that develops in patients admitted to the
intensive care unit.VAP is the most common nosocomial infection in the
ICU [1,2]. Ventilator-associated pneumonia is the second most common
nosocomial infection which contains 86% of nosocomial pneumonia [3].
Furthermore, VAP is usually
acquired in hospital settings approximately 48-72 hours aftermechanical
ventilation.VAP occurs in patients who are ventilated either by an
endotracheal tube or tracheostomy [4,5]. It is worth mentioning that the
mortality rate associated with VAP ranges from 24 to 76%, and is even
higher among critically ill patients [5,6]. In addition to the increased
risk of death, the disease causes increase ICU lengths of stays (LOS)
from 4to 13days [3]. It also increases the hospital costs and the need
for extra hospital care procedures indirectly [1].
According to the published report in 2014 by the
International Consortium Controlling Hospital Infections
(INICC), the overall rate of ventilator-associated pneumonia was
also higher (16.8 per 1000 days using a ventilator). Using such
an index to measure the risk is due to the fact that if patients use
a ventilator more than two days, they will suffer from VAP [1].
VAP is categorized into two kinds of early-onset VAP and
late-onset VAP. Early-onset VAP occurs during the first four days
of mechanical ventilationand is usually caused by antibiotic
sensitive bacteria. Late-onset VAP develops five or more days
after the initiation of mechanical ventilation and is caused by
multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens [4,5].
The main causes of VAP include: bacterial colonization of
the aero digestive tract and aspiration of contaminated oral
secretions into the lower airways because endotracheal tubes
used to ventilate neonates which are not cuffed [4]. The major
causes of acquiring endemic VAP is oropharyngeal colonization
by the endogenous flora or by pathogens acquired exogenously
from the intensive care unit environment, especially the hands
or apparel of health-care workers, contaminated respiratory
equipment, hospital water or air. The stomach represents
a potential site of secondary colonization and reservoir of
nosocomial Gram-negative bacilli. Absorption of microbe-laden
oropharyngeal, gastric or tracheal secretions around the cuffed
endotracheal tube into the normally sterile lower respiratory
tract results in most cases of endemic VAP [1,7,8].
In order to control and reduce the incidence of VAP, numerous
institutions have attempted to give medical guidelines. The
United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
(CDC) has also published a guide entitled “A Guide to prevent
nosocomial pneumonia” in 2003. Some of the guidelines for the
prevention of VAP are listed in the mentioned guide include:
The angle of the head of the bed, the cuff pressure inside the
tracheal tube, the ventilator circuit changes, oral care (including
brushing teeth, using Chlorhexidine, applying water soluble
mouth moisturizer), rotating the position of oral endotracheal
tube, sedation reduction, consuming stress ulcer prophylaxis
drugs, consuming venous thrombo embolism Prophylaxis drugs,
suctioning contaminated secretions, evaluating the patient’s
readiness daily to wean them off the ventilator, using and
changing antibacterial filter, and heat and moisture exchangers
[9].
The guidelines are used as a combination of a number of
guidelines in the intensive care unit, and the results have been
effective in reducing the incidence of VAP. Despite such guidelines,
the rate of the incidence of VAP is still significant. On the one
hand, the number of different guidelines and implementation
of each of them in different hours and conditions, and human
error in remembering responsibilities increase the probability
of not implementing the guidelines correctly and timely. On the
other hand, due to the constant shifts of the staff in the intensive
care unit, and lack of coordination between staff and not
informing each other of carrying out the guidelines and the timeof their implementation, the incidence of ventilator-associated
pneumonia is inevitable [10].
Some of the possible errors include: notchangingthe
ventilator circuit and antibacterial filter timely, ignoring the
guidelines for cleaning patients’ mouth, and not adjusting the
angle of the head of the bed.
One of the strategies to reduce human errors and create
coordinationamong thestaff in order to perform accurate
and timely guidelines is the use of informatics tools such as
dashboard software, reminders and alarms. The purpose of
this study was to use dashboard software to reduce ventilatorassociated
pneumonia.
This study was conducted through a library method and
searching the databases of PubMed, Science Direct, Google
Scholar and the key words of dashboard, ventilator associated
pneumonia, VAP reduction dashboard, VAP dashboard,
pneumonia, alert, ICU, ventilator and monitoring software. A
total number of 58 articles were available. After investigating the
quality of the articles based on the references and conforming
their objectives with the present study, 23 articles published
from 2003 to 2014 were chosen.
The present study first identified different kinds of
dashboards in the field of health and the studies providing
dashboards to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia in the
ICU were studied in terms of the design, sample, intervention,
prominent features of the dashboard software of the studies, the
results of the application of dashboard and its impacts to reduce
ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Increasingly the healthcare organizations define dashboard
software as a means to measure and improve care quality.
Dashboard software allows easy access to various databasesin a
single display format [11]. The superiority of the display format
of the data to their numerical format and providing real-time
information are the most important features distinguishing
between dashboard software and decision support systems in
the field of health.In such applications, the data related to the
patients, health care professionals and equipment in the field of
healthcare used [12].
Dashboard applications in the field of health are used in
the two forms of “Quality dashboard” and “ Clinical dashboard”.
Quality dashboard is a visual display of the quality indices that
allows managers to identify areas needing improvement [13].
For example, in England quality dashboard is established by
the Ministry of Health to evaluate the performance of health
care providers including the ratio of the nurses to the beds for
patients, the ratio of physicians to the number of beds, the results
of the staff audit and patients and the incidence of nosocomial
infections and mortality rate [14]. Ultimately, the information is
used by senior authorities to decide on the quality and output of
health service providers [13].
Clinical dashboard applications are used with the aim of
providing practical and timely information in order to create
the right conditions to decide on the daily performance of health
staff improving the quality of care for the patients [13]. Such
tools help the health care staff to do and record the procedures
of medical guidelines and protocols in detail and when it is
required [10].
The ICU is also one of the subordinate vital health areas of
the users of dashboard applications in a way that the processes
of the ICU done by service providers and the management of
its resources can be efficiently managed through dashboard
application. For example, beds in the ICUare considered as
one of the crucial sources of the hospital. Thus, the following
problems occur: the timely rejection of or early discharge of
the current ICU patients to accept new emergency patients.In
order to reduce such problems, it is so helpful to monitor and
managethe beds through dashboard in a network of municipal
and provincial hospitals [15].
The dashboard software for the prevention of ventilatorassociated
pneumonia is also one of the varieties of dashboard
applications used in ICU. The application provides a real-time
and graphic display of the information (a combination of text
and image) so that the ICU staff can be informed of the existing
condition with a glance and take the necessary measures. In
addition to mentioned items, reminders and alarmsin due time
of the guidelines are effective features of the application.
Numerous studies have been conducted to evaluate the
application of dashboard and its effectiveness to prevent
ventilator-associated pneumonia which has been dealt with in
the following paragraphs.
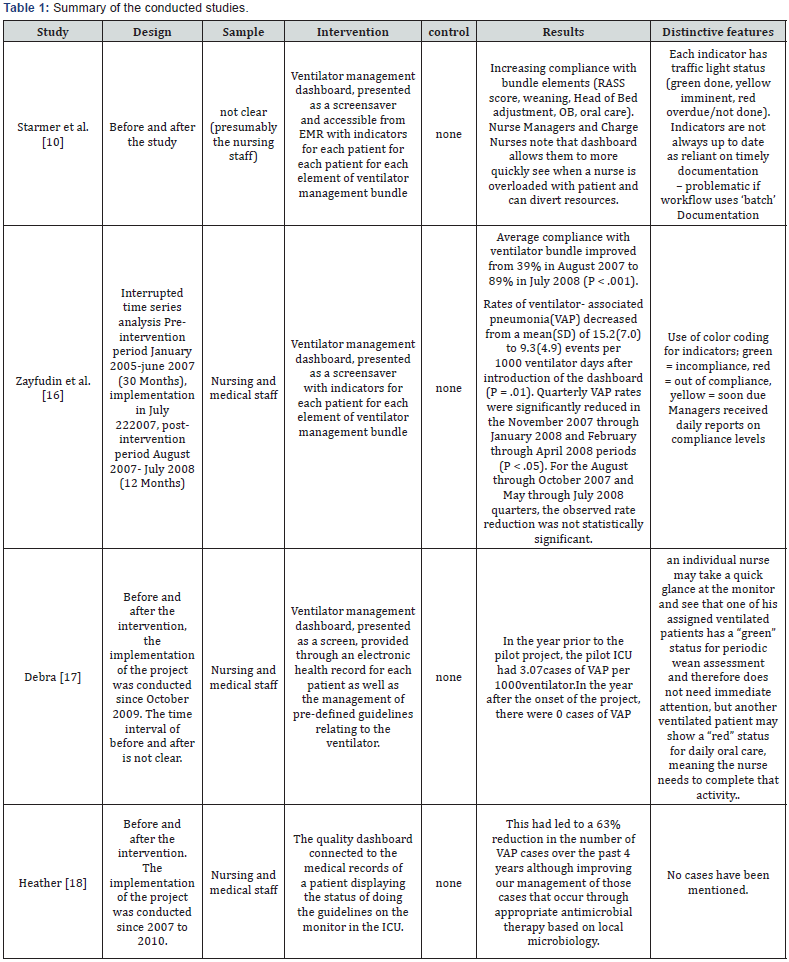
A Real-time ventilator management dashboard: “Toward
Hardwiring Compliance with Evidence-based Guidelines” is the
title of a study done by Starmer, et al. [10] in 2007. In this study,
a ventilator management dashboard application is designed to
display the patient’s condition by using the guidelines provided
by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention such as
the prevention of DVT Prophylaxis, stress ulcer prophylaxis,
sedation management and daily assessment of readiness to
exudate, adjusting the head of the bed at the angle of 35-450,
brushing the teeth and hypo pharyngeal suctioning. Each
guideline based on its nature is done by several employees of
the ICU at different times. Therefore, the dashboard application
coordinates the individuals and also shows proper colors for
the status of doing the guidelines. The dashboard utilizes data
from various sourcesystems already in use by clinical personnel,
including clinical documentation systems and computerized
provider order entry (CPOE). These systems pass results
through an interface engine which in turn routes the results to
subscriber systems. The system also provides the possibility of
reporting based on the individuals and processes. By September
2007, dashboard software was installed on all adult intensive
care units which increased the number of procedures [10].
“Implementation of a Real-time Compliance Dashboard to
Help Reduce SICU Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia with the
Ventilator Bundle” is the title of the study by Zaydfudim, et al.
[16] through the dashboard application in a previous study in
2009. During the study, guidelines for the prevention of VAP
improved from 39% in 2007 to 89% in 2008. In addition, the
incidence of VAP reduced by 39 percent from 15.2 to 9.3 cases
per 1,000 days using a ventilator in the intensive care unit [16].
“Real-Time, Right Care” is the title of a study carried out
by Debra, et al. [17] in 2013 with the support of Health East
institution and provision of dashboard application to manage
guidelines for the prevention of VAP. The Ventilator-Associated
Pneumonia (VAP) Quality Monitor is a software tool that
monitors clinical transactions as they occur within Health East’s
electronic medical record (EMR) system and uses embedded
logic to evaluate the transactions against pre-defined processes
of care related to preventing VAP. The information is constantly
available via a wall-mounted monitor, or it can be displayed on
demand at any user’s desktop. z
For instance, nurses may take a quick glance at the monitor
and see status. Such immediate feedback helps the nurses to
take measures when necessary. The guidelines of adjusting the
head of the bed, daily sedation vacations and the assessment
of readiness to exudate, consuming anticoagulants and drugs
preventing peptic ulcer disease prophylaxis, venous thrombosis
prophylaxis, daily oral care with Chlorhexidine were considered
in this study. In the year prior to the pilot project, the pilot ICU
had 3.07 cases of VAP per 1,000 ventilators. In the year after the
onset of the project, there were 0 cases of VAP [17].
“Infection Control for Critically Ill Trauma Patients” is
the title of a study by Heather in 2012, conducted through
describing a comprehensive multi-disciplinary approach for VAP
focused on prevention, diagnosis and appropriate management.
For the trauma surgical population, VAP continues to be one of
the most challenging hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), with
the incidence rate of the highest in the burn (7.4 cases per 1000
days using a ventilator), trauma (6.5 cases per 1000 days using
a ventilator), and neurosurgical (3.8 cases per 1000 days using a
ventilator) intensive care units (ICUs) compared with an overall
pooled mean rate of 2.2 cases per 1000 days using a ventilator
Regarding the issue that the prevention of VAP requires
coordinated efforts between providers, nursing staff and
respiratory therapists, in this study, the elements of adjusting
the head of bed at more than 300, a daily sedation awakening
trial and the assessment of readiness to exudate, oral care with
Chlorhexidine, peptic ulcer disease prophylaxis and deep vein
thrombosis prophylaxis were considered. The quality dashboard
application is accessible through the electronic medical record
of the patient and the status of doing the guidelines is shown on
monitors mounted throughout the ICUs. The result of the study
indicates a 63% reduction in the absolute number of VAP cases
and also a reduction in the treatment period from 12 days to10days during the 4 years of using the dashboard application
[18].
Two more studies on the clinical dashboard applications of
the ICU processes are provided: “Clinical Dashboards: Impact on
Workflow, Care Quality, and Patient Safety” is the title of a study
performed by Egan, the researcher of Massachusetts General
Hospital in 2006.In the same year, Massachusetts General
Hospital used the dashboard application in the operating room
in order to monitor and display essential dataof the patients
automatically on the screen. Moreover, the application receives
processes, integrates, and shows a wide range of the data of
patients on the screen. During the study, the mentioned idea
of using the dashboard application was extended to the ICU.
According to Egan there are not only many similarities between
the workflow of the ICU and the workflow of operating room,
but also more complexities in many cases; therefore, providing
dashboard management application is required for the ICU.
The following features are considered for the proposed
application:
Making a coordination among the health care team, data
management of the patient such as allergies, daily status of
the patient, medical history, medication regimen, the dose
of injections, the results of tests, prescribed treatment plan,
adjusting devices such as a ventilator and displaying the data
depending on the user (doctor, nurse and anesthesiologist) [19].
“Designing and evaluatingan electronic application of
nursing process: a step to improve learning and nursing care” is
the title of a study conducted by Mazloum, et al. [20] in Mashhad
in 1393. Mazloum has expressed the reason of performing
the study was thatthere is a need for the nursing field to use
an electronic application of nursing process-mail software to
use the nursing process and expressed the mismatch between
external applications but the available foreign applications are
not suitable for the country in terms of language, cultural and
social factors and clinical conditions. The study was conducted
in two parts: designing and evaluating the application.The first
part of the study was carried out in the four stages of “developing
nursing process in accordance with the application”, “designing
algorithm”, “test run” and “final reform”. The second part is also
done with the participation of 20 students and nurses in the ICU
at Ghaem Hospital of Mashhad. They did the nursing processes
through the designed application for 3 patients and their
views have been collected by the questionnaire of application
evaluation.
The application includes the menus of reference information,
recording background information of the patient, recording the
nursing process, setting, alerts and the guide. The results of the
evaluation show that 81.3% of the research units evaluated the
application as good or very good generally. The most important
advantage of the application according to 90% of the nurses
is the accuracy of the electronic information compared with
the handwritten form helping to organize the problems of thepatients. According to 100% of the students, the most important
advantages of the application are its simplicity, helping the
division of responsibility, evaluating the warning signs and
preventing errors; therefore, it is possible to design a native
application for nursing processes in accordance with the health
care system with which the nurses and students are satisfied.
Moreover, the implementation of such an application helps
to increase the accuracy and reduce the errors and division of
responsibility. Such factors improve the patient care [20]. The
summary of the conducted studies is provided in Table 1.
This study was conducted to investigate the effect of
the dashboard application to reduce ventilator-associated
Pneumonia. Four investigated studies are completely in line
with the objective of the present study and two studies provide
a dashboard application to do the ICU processes.The uses of the
dashboard application based on theconducted studies in this
study suggest that the use of the dashboard application can help
toremove the factors causing VAP in ICU.
Failing to remember the guidelines and doing them properly
due can cause the colonization of bacteria in the oral mucosa
and tracheal secretions and aspiration to the lower part of the
pharynx of the patient due to the large number of guidelinesand
thus cause the patient to get VAP. The dashboard application
displays a list of guidelines and information, such as the angle of
the head of the bed, and the name and dose of drugs to ensure the
nursesso that the guidelines are done with the minimum mistake
in terms of forgetting the number of times. The change of shifts
by the specialists and nurses of the health care unit causes them
to be unaware of the status of the guidelines for the prevention
of VAP in the previous shift. So, displaying the history and status
of the current guidelines on the dashboard application due to
its information giving nature helps the nurses and specialist
prevent the errors and improves teamwork. However, if there is
not such an application, many of the members of the team would
deny the responsibility even though they are informed of the
status of the guidelines.
Dashboard application uses user accounts and controls
the access levels clarifying the mentioned cases. Doing VAP
prevention guidelines is not among the responsibility of
the nurses to document which increases the human error.
Dashboard application makes it possible to record the time
of doing the guidelines and provide a suitable environment
for documentation which will subsequently lead to doing
the guidelines timely and reducing ventilator-associated
pneumonia. In addition to the effect of dashboard application on
reducing ventilator-associated pneumonia, the continued use of
the application and the observation of positive effects make the
staff aware of the importance of documentation.
Another outcome of the use of dashboard for the prevention
of VAP is to train people in doing the guidelines timely. In fact,
emphasizing the reason to do the guidelines and its effect onthe quality of services provided by the health care staff due to
instructions, will pass better training in this regard.
Ultimately, since the focus of the application is on patients,the service providers provide systematic strategies to ensure
that all patients receive all the best care; therefore, it reduces
ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Discussion and Conclusion
Investigating the results of the performance of the
dashboard application in studied investigations, it can be said
that in the study conducted by Zaydfudim, et al. [16] in 2007,
VPA was reduced by 38 percent (from 15.2 to 9.3 cases per 1,000
days of using a ventilator) as reported.In the study carried out
by Debra, et al. [17] in 2013, VPA was reduced by 100 percent
(from 3.07 to 0 cases) as reported and it seems that it is possible
to display the dashboard on the monitor mounted in the ICU at
every moment.The long duration of the study, the high number
of nurses and its connection to patients’ medical records
increase the impacts of using dashboard application in reducing
ventilator-associated pneumonia. The environment of the study
and the work discipline of the mentioned studies were involved
in the effectiveness of the use of dashboard application to reduce
ventilator-associated pneumonia, since increasing the work
discipline in an environment makes it more difficult to change.
Due to the increasing development of IT and the influence
of information systems in the field of health andclinical care,
adding more features to the dashboard application to provide
health services in a better way and focus more on patients. The
mobile version of the dashboard application can be used on the
nurses’ tablets or cell phones and makes it possible to use it
immediately beside patients’ bed. In such a condition, the time
of doing the guidelines is recorded with less time error and also
more quickly and easily.
Connecting the dashboard application to patients’ medical
file allows you to get the information and makes it possible to
record the summary of the data of doing the guidelines in the
medical file. Providing high-rank managers with the management
information of the trend graphs of the incidence of disease makes
them aware of the effectiveness of the nursing processes done
in the health care units and proper decision making. Since the
number of health care nurses is not usually equal to the number
of nurses, it is quicker to enter the data into the application
through hardware systems such as the use of sensors to check
the angle of the head of the bed or data transfer technologies of
NFC on the ventilator circuit and heat and moisture exchangers
that can be helpful in recording the time of change.
Furthermore, connecting the dashboard application to DSS
systems can help to change the number of times the guidelines
are practiced and the way to do it based on the condition of
patients.
Providing a web-based dashboard application facilitates the
access and online use and can be used to improve the application.
Finally, using the dashboard application can reduce the rate
of the incidence of different infections and do the management
processes in the field of health in a better way. For example, the
dashboard applicationcan also be effective in preventing other
infections such as catheter-related urinary tract infections, the
most common nosocomial infections.
To know more about Open Access International
Journal of Pulmonary & Respiratory Sciences please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ijoprs/index.php


Comments
Post a Comment